Introduction
After developing your app locally on your machine, the next step is to deploy it to the web so that others can access it.
In this section, we'll walk you through the steps to deploy your Wasp app.
Wasp app structure
Before we start, let's understand what Wasp generates when it builds your app.
What we call a "Wasp app" consists of three different parts:
-
Client app
- It's a single-page application (SPA), built using React. It's what the user sees and interacts with.
- It's usually served by some static file server or you can host it on a CDN like Cloudflare or Netlify.
-
Server app:
- The backend of your app, built using Express on Node.js.
- It handles requests from the client app, interacts with the database, and returns responses.
- It comes with a ready-to-use
Dockerfileso you can easily package it and deploy it anywhere where Docker is supported.
-
Database:
- Wasp uses PostgreSQL as its production database.
- You can host the database on your own server or use a cloud service.
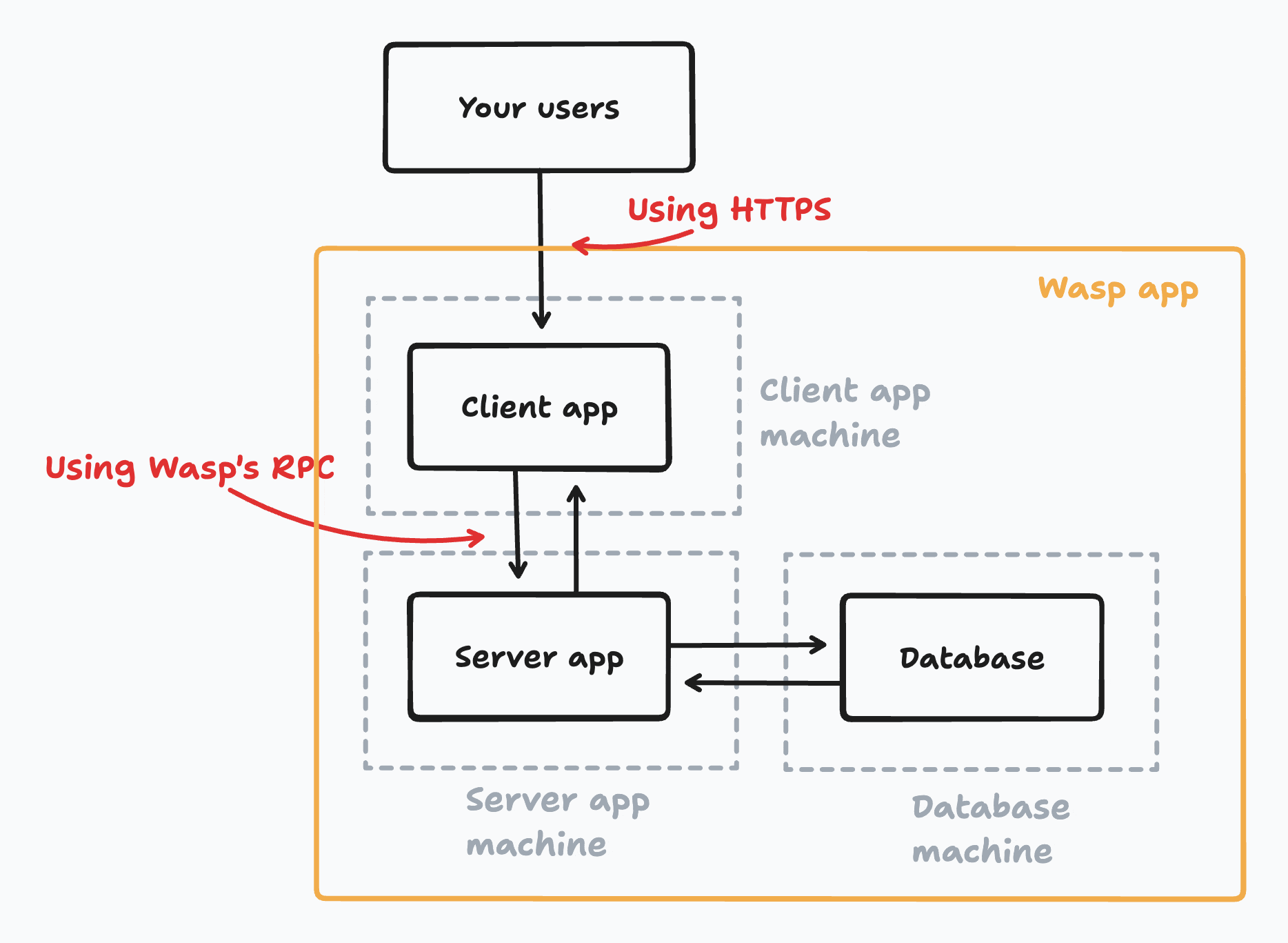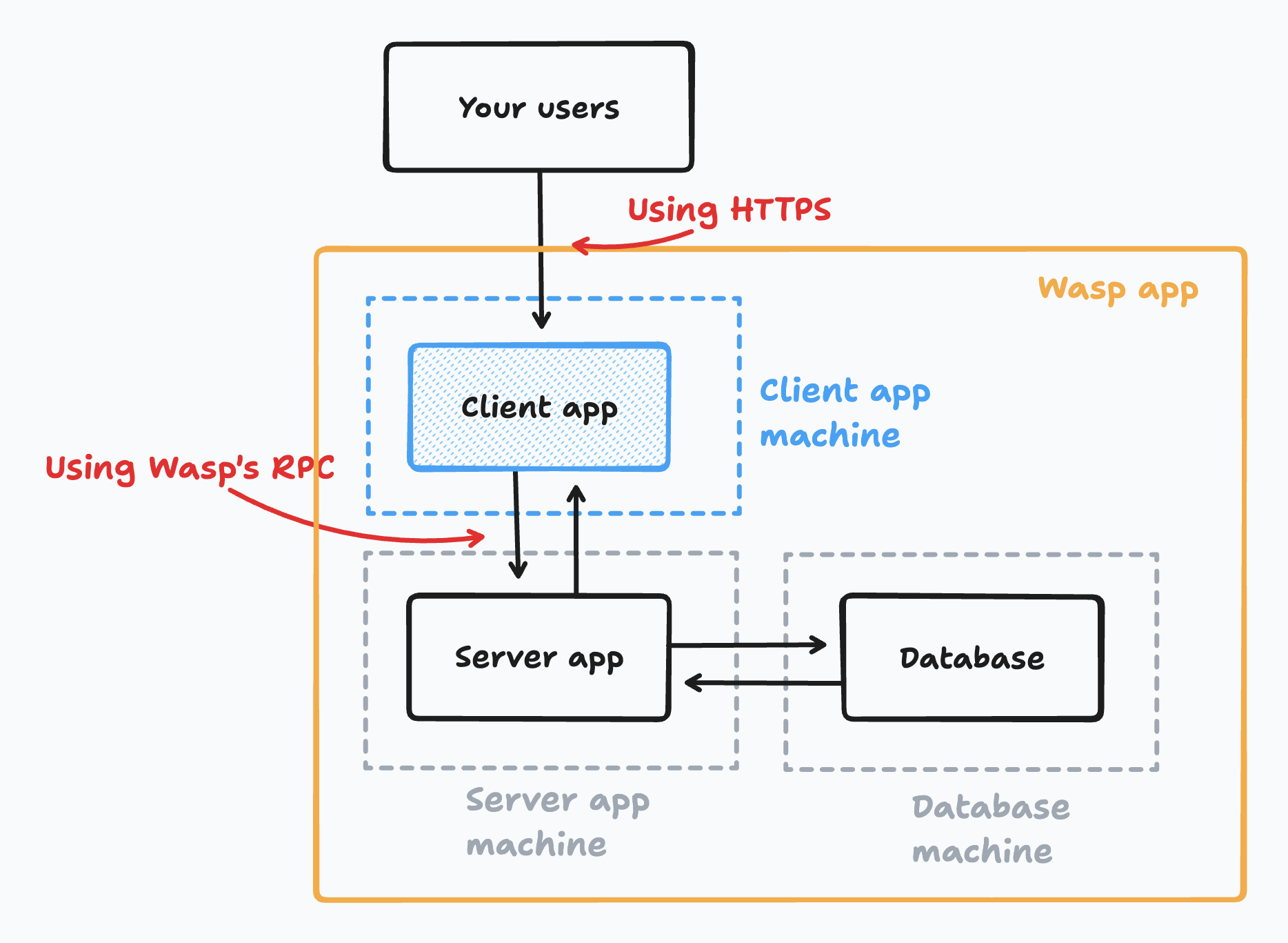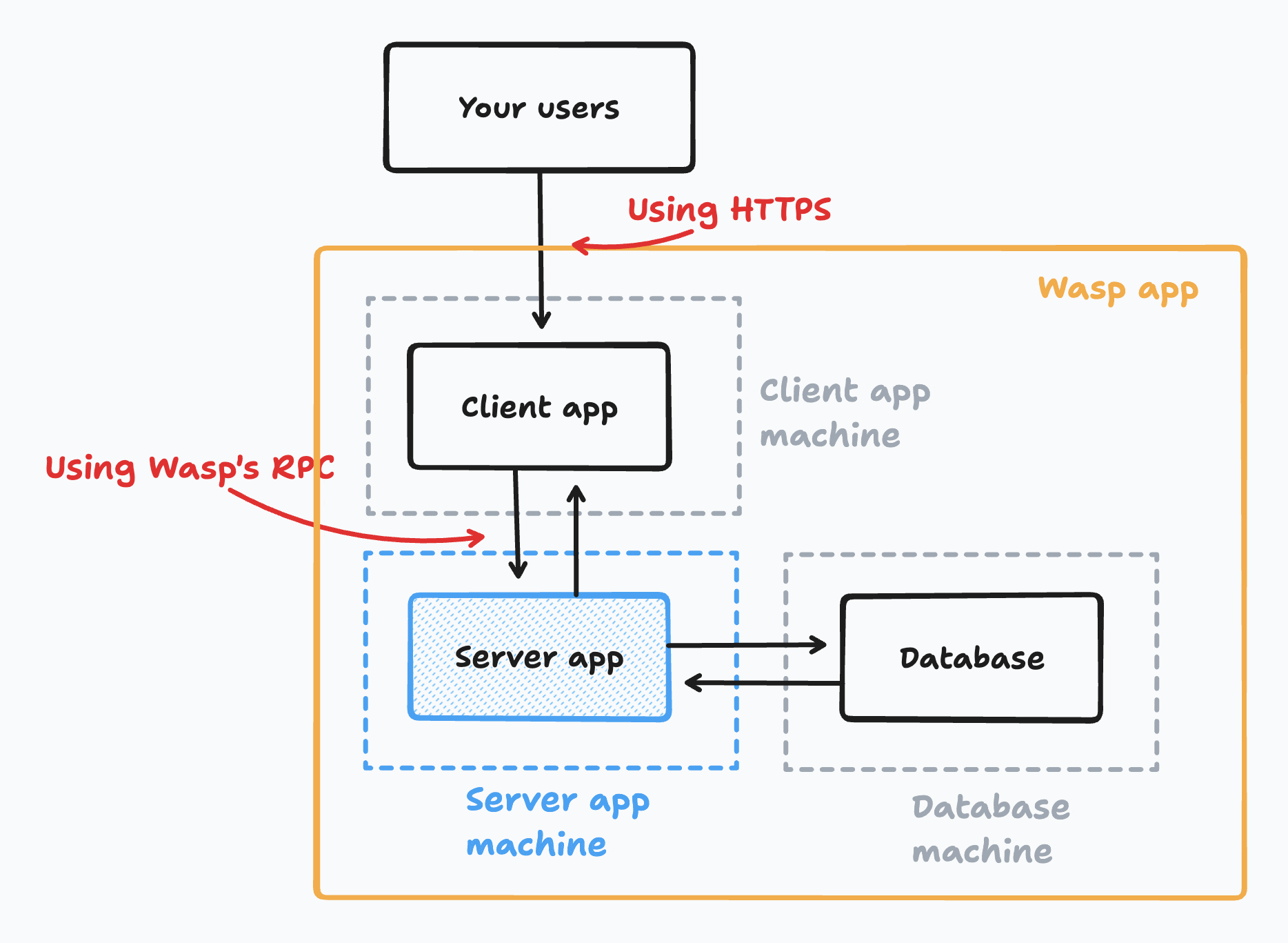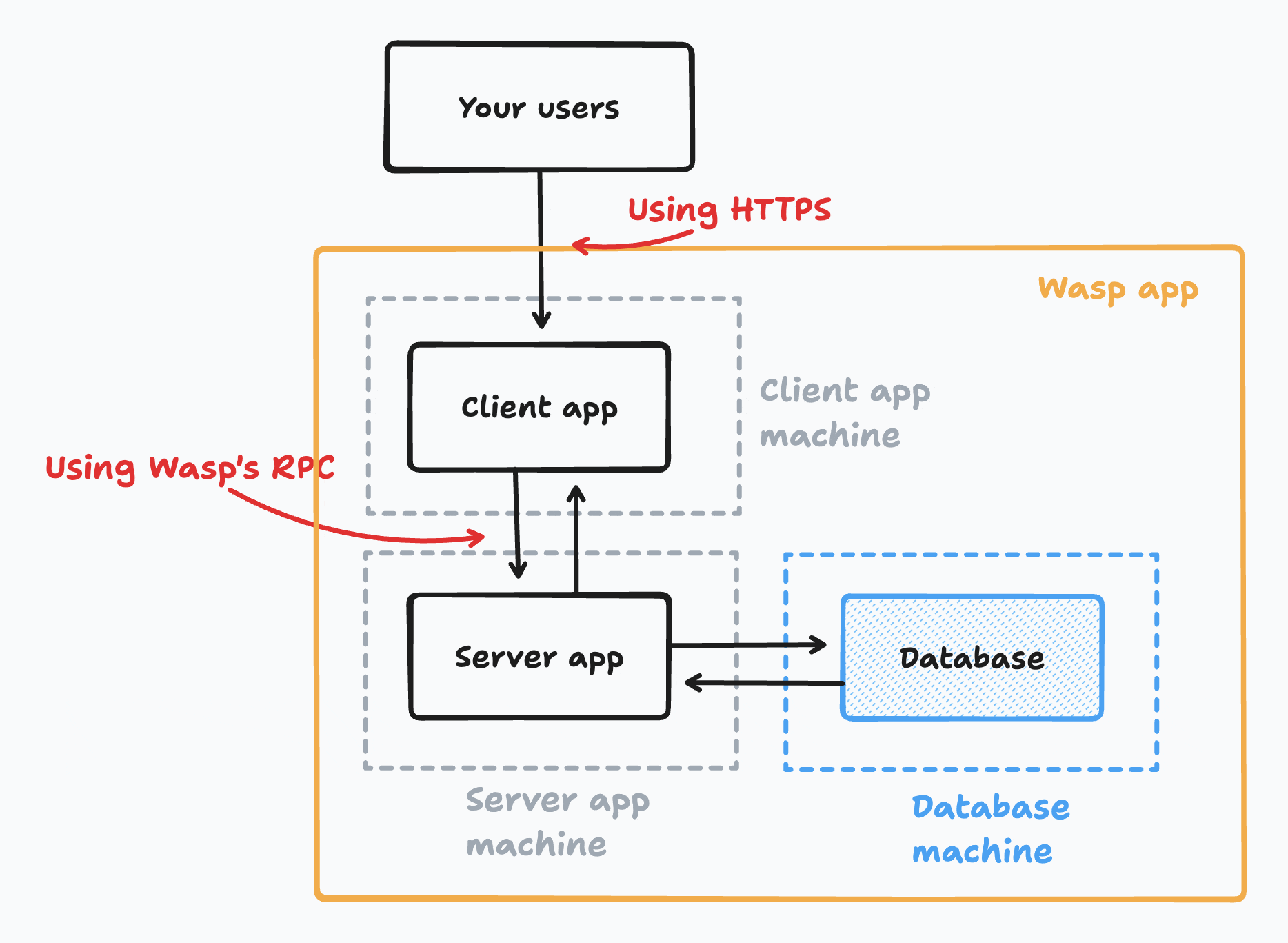
The thing to take away from this: the client app and server app are separate applications that communicate with each other over HTTP. This means you can deploy them on the same or different servers, depending on your needs.
We'll show you different ways of how deploy your app in the deployment methods section.
Server needs to be able to communicate with the database, we'll show you how to set that up using env variables.
Deploying your app
In the following sections, we'll go through all the different things you need to know about deployment:
- How env variables work in production - they are different than using .env files in development.
- Production database setup - how migrations work, how to connect to the database, etc.
- Different deployment methods (using Wasp's CLI, cloud services, self-hosting, etc.)
- How to set up CI/CD for your app - automatically deploy your app when you push to your Git repository.
- Some extras like custom domains, CDN, etc.