Self-Hosted
If you have your server or rent out a server, you can self-host your Wasp apps. Self-hosting your apps gives you full control over your apps and their data. It can be more cost-effective than a cloud provider since you can deploy multiple apps on a single server. However, you'll need to manage the server yourself, which can be time-consuming and require some technical knowledge.
What you'll need
To successfully self-host your Wasp app, you need to have the following:
- A server with a public IP address.
- There are many cloud providers you can use to rent a server. Some popular ones are AWS, DigitalOcean, OVH, and Hetzner.
- A domain name, for example,
myapp.com(needed for HTTPS support).
Self-hosting steps
To self-host your Wasp app, you need to follow these general steps:
-
Get your app's code on the server.
- How you do this depends on your setup, we'll explore a few methods in the next section.
-
Run your client and server apps on the server. Run the database on the server or use a managed database service.
- We'll use Docker to run the server app and the database, but you can run them without Docker if you prefer.
-
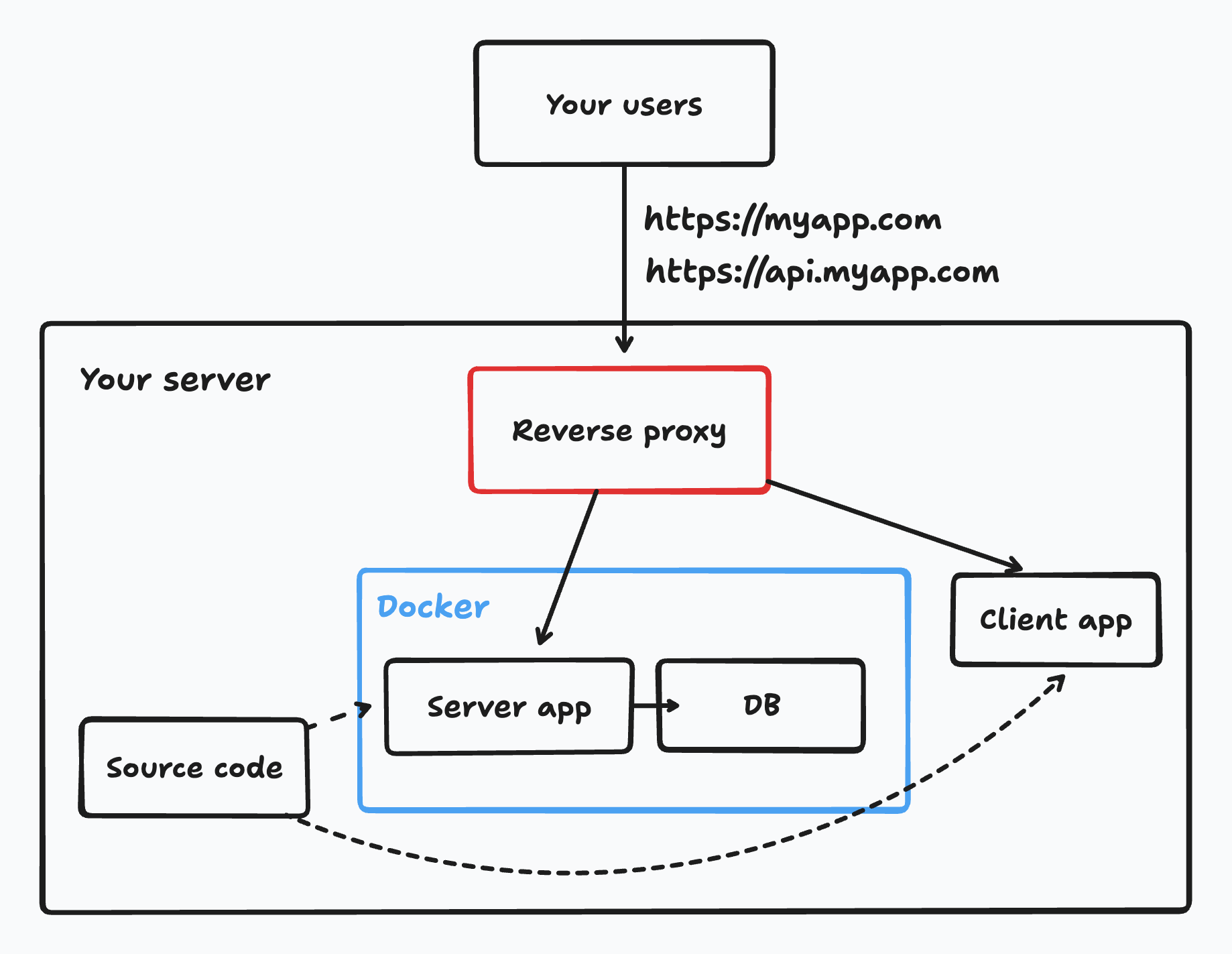
Set up a reverse proxy on the server to be able to use a domain name with HTTPS for your app.
-
Configure the env variables on your server for the server app.
Deployment methods
We'll explore a few methods you can use to self-host your Wasp app. The first method is the most straightforward: you manually set up everything on your server. The other two methods require you to install and configure a self-hosted PaaS on your server and then use that to deploy apps to it.
Simple setup
In this setup, you do all the steps on the server: you install Docker, set up the server env variable, set up a reverse proxy, and run your app. This is a very manual process, but you'll learn how everything works.
Overview of the steps
On your server:
- Install Docker, Node.js and Wasp CLI.
- Get your app's source code.
- We recommend using Git to clone your app's repository and then pulling the latest changes when you want to deploy a new version. You can use any other method to get your app's code on the server.
- Build your app with
wasp build. - Build and run the server app.
- Wasp gives you a
Dockerfilein the.wasp/outdirectory that you can use to build and run the server app. - We are using Docker to run the server app, but you can run it without Docker if you prefer - just make sure to replicate the setup in the
Dockerfile. - When you run the server app with Docker, you need to setup the server env variables. You can do this with a
.envfile or by passing the env variables directly to thedocker runcommand.
- Wasp gives you a
- Start the database on the server or use a managed database service.
- We usually run the database in Docker on the same server, but you can run the database directly on the server.
- You can also use a managed database service which you can connect to from your server. This is a great option if you don't want to manage the database yourself, but it can be more expensive.
- Build the client app into static files.
- Wasp outputs the client app in the
.wasp/out/web-appdirectory.
- You should build the client app into static files.
- Wasp outputs the client app in the
- Install and set up a reverse proxy to serve your client and server apps.
- Point your domain(s) to your server's IP address.
- We recommend setting
myapp.comfor the client andapi.myapp.comfor the server. - The reverse proxy should serve the client app on
myapp.comand proxy requests to the server app onapi.myapp.com. Make sure your env variables are using these client and server URLs.
- We recommend setting
Check out one of our step-by-step guides for more details:
Deploying Wasp with Docker on your server »
Uses Ubuntu, Git, Caddy, Docker
Coolify
Coolify is a deployment tool (self-hosted PaaS) that you run on your server. It makes it easier to deploy multple apps on your server. It has a nice looking UI and it helps you with managing your deployments.
Overview of the steps
- Install Coolify on your server.
- Create your Coolify apps (client, server, and database).
- You can run the database with Coolify on the same server, but you can run the database directly on your server or use a managed database service.
- In Coolify, set up the server app env variables.
- You can set up the env variables in the Coolify UI, check out which env variables are required.
- Set up some sort of CI/CD (for example Github Actions) to:
- build and upload your Docker images,
- trigger Coolify to pull the Docker images and deploy them.
- Point your domain to your server's IP address.
- We recommend setting
myapp.comfor the client andapi.myapp.comfor the server. - Make sure to set the domains in the Coolify UI for the client and the server apps.
- Make sure to set the env variables for the client and the server URLs correctly.
- We recommend setting
Check out one of our step-by-step guides for more details:
Deploying Wasp with Coolify on your server »
Uses Coolify, Github Actions, Github Container Registry
CapRover
CapRover is a deployment tool (self-hosted PaaS) that you run on your server. It makes it easier to deploy multple apps on your server. It has a nice looking UI and it helps you with managing your deployments.
Overview of the steps
- Install CapRover on your server.
- Create your CapRover apps (client, server, and database).
- You can run the database with CapRover on the same server, but you can run the database directly on your server or use a managed database service.
- Set up the server env variables.
- You can set up the env variables in the CapRover UI, check out which env variables are required.
- Set up some sort of CI/CD (for example Github Actions) to:
- build and upload your Docker images to a Docker registry,
- trigger CapRover to pull the Docker images and deploy them.
- Point your domain to your server's IP address.
- We recommend setting
myapp.comfor the client andapi.myapp.comfor the server. - Make sure to set the domains in the CapRover UI for the client and the server apps.
- Make sure to set the env variables for the client and the server URLs correctly.
- We recommend setting
Check out one of our step-by-step guides for more details:
Deploying Wasp with Caprover on your server »
Uses Caprover, Github Actions, Github Container Registry
Database setup
In all of the guides, we run the database on your server. When you run the database on your server, you need to take care of backups, updates, and scaling. We suggest setting up PostgresSQL periodic backups and/or taking snapshots of your server's disk. In case something bad happens to your server, you can restore your database from the backups.
If you prefer not to manage the database yourself, you can use a managed database service. The service provider takes care of backups, updates, and scaling for you but it can be more expensive than running the database on your server. Some popular managed database services are AWS RDS, DigitalOcean Managed Databases, and Supabase.