Prisma Schema File
Wasp uses Prisma to interact with the database. Prisma is a "Next-generation Node.js and TypeScript ORM" that provides a type-safe API for working with your database.
With Prisma, you define your application's data model in a schema.prisma file. Read more about how Wasp Entities relate to Prisma models on the Entities page.
In Wasp, the schema.prisma file is located in your project's root directory:
.
├── main.wasp
...
├── schema.prisma
├── src
├── tsconfig.json
└── vite.config.ts
Wasp uses the schema.prisma file to understand your app's data model and generate the necessary code to interact with the database.
Wasp file and Prisma schema file
Let's see how Wasp and Prisma files work together to define your application.
Here's an example schema.prisma file where we defined some database options and two models (User and Task) with a one-to-many relationship:
datasource db {
provider = "postgresql"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client-js"
}
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
tasks Task[]
}
model Task {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
description String
isDone Boolean @default(false)
user User @relation(fields: [userId], references: [id])
userId Int
}
Wasp reads this schema.prisma file and extracts the info about your database models and database config.
The datasource block defines which database you want to use (PostgreSQL in this case) and some other options.
The generator block defines how to generate the Prisma Client code that you can use in your application to interact with the database.
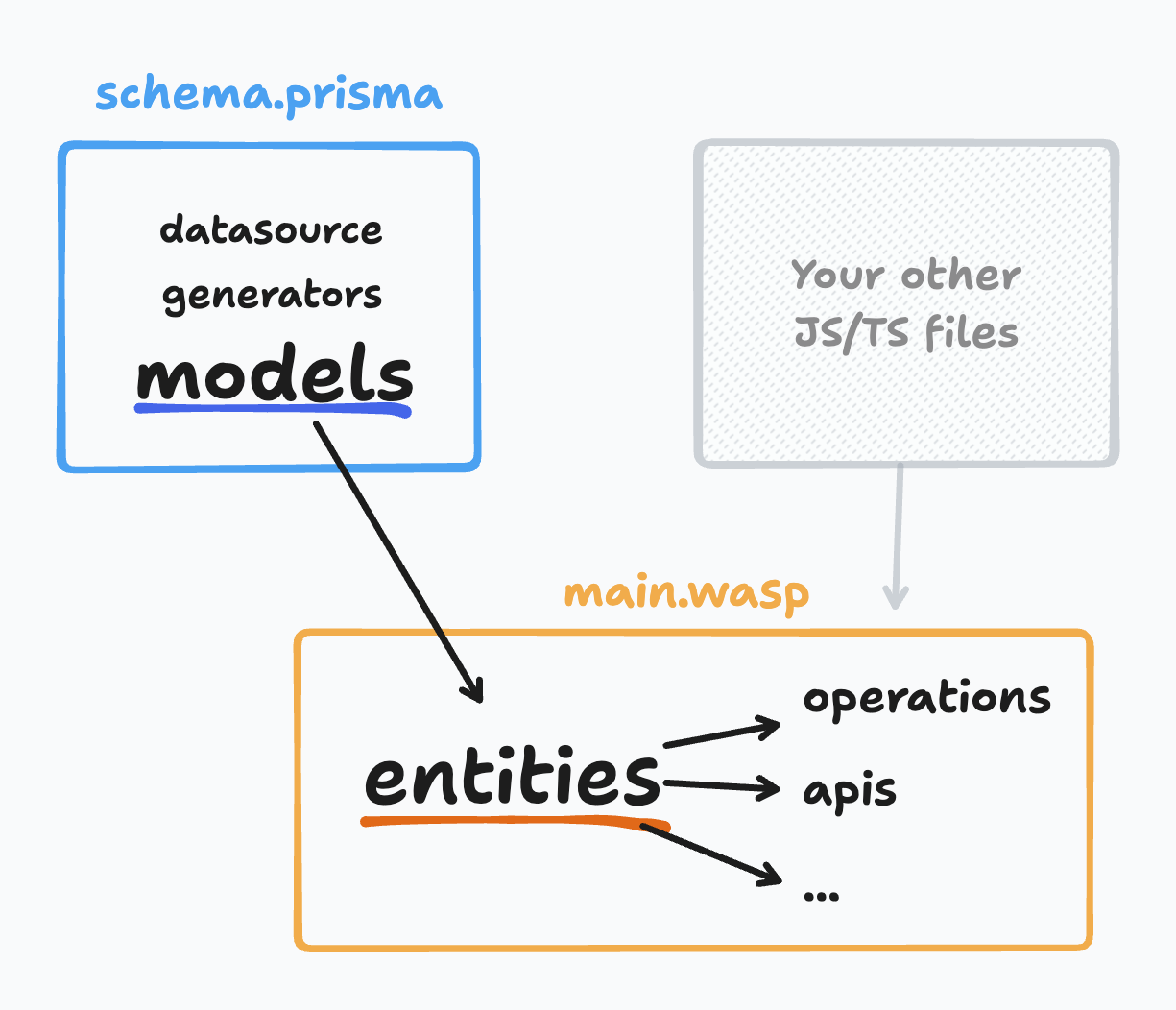
Finally, Prisma models become Wasp Entities which can be then used in the main.wasp file:
app myApp {
wasp: {
version: "^0.21"
},
title: "My App",
}
...
// Using Wasp Entities in the Wasp file
query getTasks {
fn: import { getTasks } from "@src/queries",
entities: [Task]
}
job myJob {
executor: PgBoss,
perform: {
fn: import { foo } from "@src/workers/bar"
},
entities: [Task],
}
api fooBar {
fn: import { fooBar } from "@src/apis",
entities: [Task],
httpRoute: (GET, "/foo/bar/:email")
}
In the implementation of the getTasks query, Task is a Wasp Entity that corresponds to the Task model defined in the schema.prisma file.
The same goes for the myJob job and fooBar API, where Task is used as an Entity.
To learn more about the relationship between Wasp Entities and Prisma models, check out the Entities page.
Wasp-specific Prisma configuration
Wasp mostly lets you use the Prisma schema file as you would in any other JS/TS project. However, there are some Wasp-specific rules you need to follow.
The datasource block
datasource db {
provider = "postgresql"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}
Wasp takes the datasource you write and use it as-is.
There are some rules you need to follow:
- You can only use
"postgresql"or"sqlite"as theproviderbecause Wasp only supports PostgreSQL and SQLite databases for now. - You must set the
urlfield toenv("DATABASE_URL")so that Wasp can work properly with your database.
The generator blocks
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client-js"
}
Wasp requires that there is a generator block with provider = "prisma-client-js" in the schema.prisma file.
You can add additional generators if you need them in your project.
The model blocks
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
tasks Task[]
}
model Task {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
description String
isDone Boolean @default(false)
user User @relation(fields: [userId], references: [id])
userId Int
}
You can define your models in any way you like, if it's valid Prisma schema code, it will work with Wasp.
The enum blocks
As our applications grow in complexity, we might want to use Prisma enums to closely define our app's domain. For example, if we had a Task model with a boolean isDone, and we wanted to start to track whether it is in progress, we could migrate the field to a more expressive type:
enum TaskStatus {
NotStarted
Doing
Done
}
model Task {
...
state TaskStatus @default(NotStarted)
}
Make sure to check Prisma's enum compatibility with your database. If it works with Prisma, it will work with Wasp.
How to use enums in your code
If you need to access your enum cases and their values from your server, you can import them directly from @prisma/client:
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
import { TaskState } from "@prisma/client";
import { Task } from "wasp/entities";
export const getOpenTasks = async (args, context) => {
return context.entities.Task.findMany({
orderBy: { id: "asc" },
where: { NOT: { state: TaskState.Done } },
});
};
import { TaskState } from "@prisma/client";
import { Task } from "wasp/entities";
import { type GetTasks } from "wasp/server/operations";
export const getOpenTasks: GetTasks<void, Task[]> = async (args, context) => {
return context.entities.Task.findMany({
orderBy: { id: "asc" },
where: { NOT: { state: TaskState.Done } },
});
};
You can also access them from your client code:
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
import { TaskState } from "@prisma/client";
const TaskRow = ({ task }) => {
return (
<div>
<input
type="checkbox"
id={String(task.id)}
checked={task.state === TaskState.Done}
/>
{task.description}
</div>
);
};
import { TaskState } from "@prisma/client";
import { Task } from "wasp/entities";
const TaskRow = ({ task }: { task: Task }) => {
return (
<div>
<input
type="checkbox"
id={String(task.id)}
checked={task.state === TaskState.Done}
/>
{task.description}
</div>
);
};
Wasp only supports /// in the leading position:
model User {
/// The unique identifier for the user.
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
}
However, Wasp does not support /// comments in the trailing position:
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement()) /// This is not supported
}
We are aware of this issue and are tracking it at #3041, let us know if this is something you need.
Prisma preview features
Prisma is still in active development and some of its features are not yet stable. To enable various preview features in Prisma, you need to add the previewFeatures field to the generator block in the schema.prisma file.
For example, one useful Prisma preview feature is PostgreSQL extensions support, which allows you to use PostgreSQL extensions like pg_vector or pg_trgm in your database schema:
datasource db {
provider = "postgresql"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
extensions = [pgvector(map: "vector")]
}
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client-js"
previewFeatures = ["postgresqlExtensions"]
}
// ...
Read more about preview features in the Prisma docs here or about using PostgreSQL extensions here.