Wasp supports e-mail authentication out of the box, along with email verification and "forgot your password?" flows. It provides you with the server-side implementation and email templates for all of these flows.
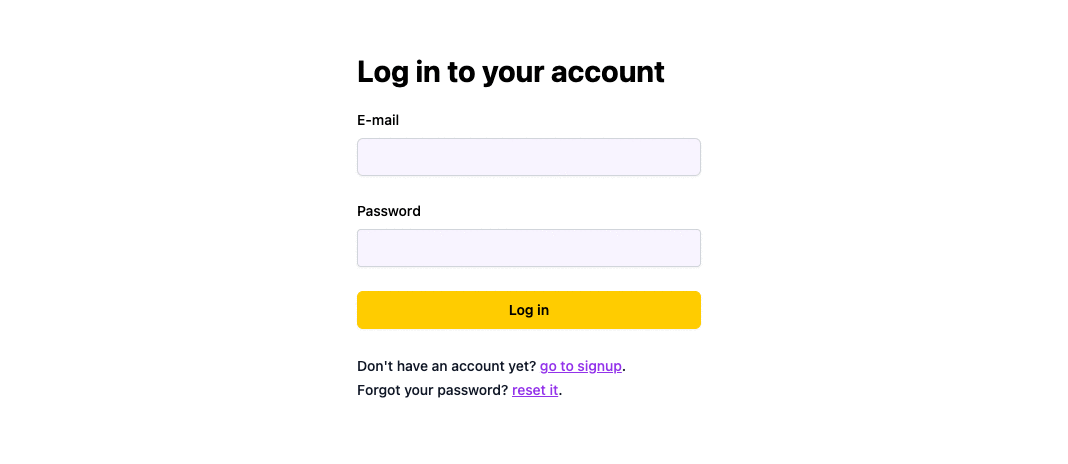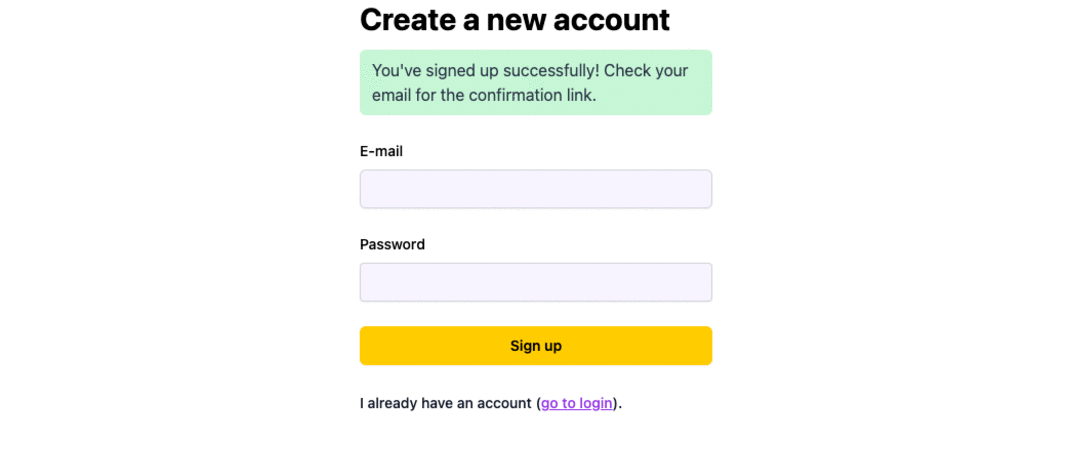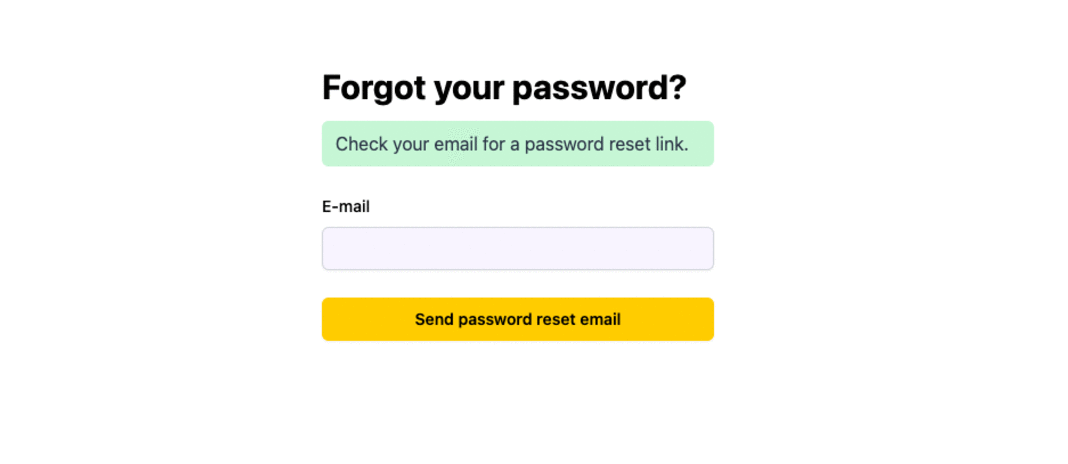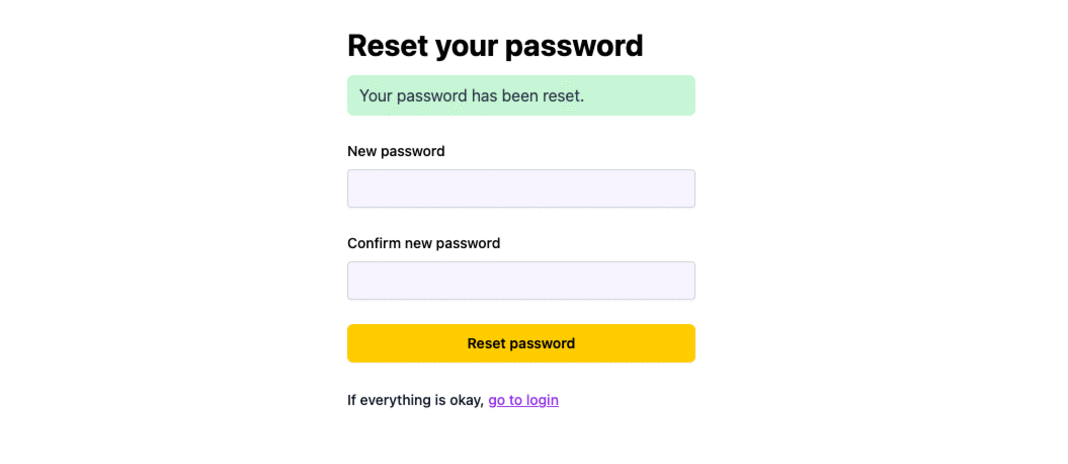
If a user signs up with Google or Github (and you set it up to save their social provider e-mail info on the User entity), they'll be able to reset their password and login with e-mail and password ✅
If a user signs up with the e-mail and password and then tries to login with a social provider (Google or Github), they won't be able to do that ❌
In the future, we will lift this limitation and enable smarter merging of accounts.
Setting Up Email Authentication
We'll need to take the following steps to set up email authentication:
- Enable email authentication in the Wasp file
- Add the user entity
- Add the routes and pages
- Use Auth UI components in our pages
- Set up the email sender
Structure of the main.wasp file we will end up with:
// Configuring e-mail authentication
app myApp {
auth: { ... }
}
// Defining User entity
entity User { ... }
// Defining routes and pages
route SignupRoute { ... }
page SignupPage { ... }
// ...
1. Enable Email Authentication in main.wasp
Let's start with adding the following to our main.wasp file:
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
app myApp {
wasp: {
version: "^0.11.0"
},
title: "My App",
auth: {
// 1. Specify the user entity (we'll define it next)
userEntity: User,
methods: {
// 2. Enable email authentication
email: {
// 3. Specify the email from field
fromField: {
name: "My App Postman",
email: "hello@itsme.com"
},
// 4. Specify the email verification and password reset options (we'll talk about them later)
emailVerification: {
clientRoute: EmailVerificationRoute,
},
passwordReset: {
clientRoute: PasswordResetRoute,
},
allowUnverifiedLogin: false,
},
},
onAuthFailedRedirectTo: "/login",
onAuthSucceededRedirectTo: "/"
},
}
app myApp {
wasp: {
version: "^0.11.0"
},
title: "My App",
auth: {
// 1. Specify the user entity (we'll define it next)
userEntity: User,
methods: {
// 2. Enable email authentication
email: {
// 3. Specify the email from field
fromField: {
name: "My App Postman",
email: "hello@itsme.com"
},
// 4. Specify the email verification and password reset options (we'll talk about them later)
emailVerification: {
clientRoute: EmailVerificationRoute,
},
passwordReset: {
clientRoute: PasswordResetRoute,
},
allowUnverifiedLogin: false,
},
},
onAuthFailedRedirectTo: "/login",
onAuthSucceededRedirectTo: "/"
},
}
Read more about the email auth method options here.
2. Add the User Entity
When email authentication is enabled, Wasp expects certain fields in your userEntity. Let's add these fields to our main.wasp file:
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
// 5. Define the user entity
entity User {=psl
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
email String? @unique
password String?
isEmailVerified Boolean @default(false)
emailVerificationSentAt DateTime?
passwordResetSentAt DateTime?
// Add your own fields below
// ...
psl=}
// 5. Define the user entity
entity User {=psl
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
email String? @unique
password String?
isEmailVerified Boolean @default(false)
emailVerificationSentAt DateTime?
passwordResetSentAt DateTime?
// Add your own fields below
// ...
psl=}
Read more about the userEntity fields here.
3. Add the Routes and Pages
Next, we need to define the routes and pages for the authentication pages.
Add the following to the main.wasp file:
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
// ...
// 6. Define the routes
route LoginRoute { path: "/login", to: LoginPage }
page LoginPage {
component: import { Login } from "@client/pages/auth.jsx"
}
route SignupRoute { path: "/signup", to: SignupPage }
page SignupPage {
component: import { Signup } from "@client/pages/auth.jsx"
}
route RequestPasswordResetRoute { path: "/request-password-reset", to: RequestPasswordResetPage }
page RequestPasswordResetPage {
component: import { RequestPasswordReset } from "@client/pages/auth.jsx",
}
route PasswordResetRoute { path: "/password-reset", to: PasswordResetPage }
page PasswordResetPage {
component: import { PasswordReset } from "@client/pages/auth.jsx",
}
route EmailVerificationRoute { path: "/email-verification", to: EmailVerificationPage }
page EmailVerificationPage {
component: import { EmailVerification } from "@client/pages/auth.jsx",
}
// ...
// 6. Define the routes
route LoginRoute { path: "/login", to: LoginPage }
page LoginPage {
component: import { Login } from "@client/pages/auth.tsx"
}
route SignupRoute { path: "/signup", to: SignupPage }
page SignupPage {
component: import { Signup } from "@client/pages/auth.tsx"
}
route RequestPasswordResetRoute { path: "/request-password-reset", to: RequestPasswordResetPage }
page RequestPasswordResetPage {
component: import { RequestPasswordReset } from "@client/pages/auth.tsx",
}
route PasswordResetRoute { path: "/password-reset", to: PasswordResetPage }
page PasswordResetPage {
component: import { PasswordReset } from "@client/pages/auth.tsx",
}
route EmailVerificationRoute { path: "/email-verification", to: EmailVerificationPage }
page EmailVerificationPage {
component: import { EmailVerification } from "@client/pages/auth.tsx",
}
We'll define the React components for these pages in the client/pages/auth.tsx file below.
4. Create the Client Pages
We are using Tailwind CSS to style the pages. Read more about how to add it here.
Let's create a auth.tsx file in the client/pages folder and add the following to it:
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
import { LoginForm } from "@wasp/auth/forms/Login";
import { SignupForm } from "@wasp/auth/forms/Signup";
import { VerifyEmailForm } from "@wasp/auth/forms/VerifyEmail";
import { ForgotPasswordForm } from "@wasp/auth/forms/ForgotPassword";
import { ResetPasswordForm } from "@wasp/auth/forms/ResetPassword";
import { Link } from "react-router-dom";
export function Login() {
return (
<Layout>
<LoginForm />
<br />
<span className="text-sm font-medium text-gray-900">
Don't have an account yet? <Link to="/signup">go to signup</Link>.
</span>
<br />
<span className="text-sm font-medium text-gray-900">
Forgot your password? <Link to="/request-password-reset">reset it</Link>
.
</span>
</Layout>
);
}
export function Signup() {
return (
<Layout>
<SignupForm />
<br />
<span className="text-sm font-medium text-gray-900">
I already have an account (<Link to="/login">go to login</Link>).
</span>
</Layout>
);
}
export function EmailVerification() {
return (
<Layout>
<VerifyEmailForm />
<br />
<span className="text-sm font-medium text-gray-900">
If everything is okay, <Link to="/login">go to login</Link>
</span>
</Layout>
);
}
export function RequestPasswordReset() {
return (
<Layout>
<ForgotPasswordForm />
</Layout>
);
}
export function PasswordReset() {
return (
<Layout>
<ResetPasswordForm />
<br />
<span className="text-sm font-medium text-gray-900">
If everything is okay, <Link to="/login">go to login</Link>
</span>
</Layout>
);
}
// A layout component to center the content
export function Layout({ children }) {
return (
<div className="w-full h-full bg-white">
<div className="min-w-full min-h-[75vh] flex items-center justify-center">
<div className="w-full h-full max-w-sm p-5 bg-white">
<div>{children}</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
import { LoginForm } from "@wasp/auth/forms/Login";
import { SignupForm } from "@wasp/auth/forms/Signup";
import { VerifyEmailForm } from "@wasp/auth/forms/VerifyEmail";
import { ForgotPasswordForm } from "@wasp/auth/forms/ForgotPassword";
import { ResetPasswordForm } from "@wasp/auth/forms/ResetPassword";
import { Link } from "react-router-dom";
export function Login() {
return (
<Layout>
<LoginForm />
<br />
<span className="text-sm font-medium text-gray-900">
Don't have an account yet? <Link to="/signup">go to signup</Link>.
</span>
<br />
<span className="text-sm font-medium text-gray-900">
Forgot your password? <Link to="/request-password-reset">reset it</Link>
.
</span>
</Layout>
);
}
export function Signup() {
return (
<Layout>
<SignupForm />
<br />
<span className="text-sm font-medium text-gray-900">
I already have an account (<Link to="/login">go to login</Link>).
</span>
</Layout>
);
}
export function EmailVerification() {
return (
<Layout>
<VerifyEmailForm />
<br />
<span className="text-sm font-medium text-gray-900">
If everything is okay, <Link to="/login">go to login</Link>
</span>
</Layout>
);
}
export function RequestPasswordReset() {
return (
<Layout>
<ForgotPasswordForm />
</Layout>
);
}
export function PasswordReset() {
return (
<Layout>
<ResetPasswordForm />
<br />
<span className="text-sm font-medium text-gray-900">
If everything is okay, <Link to="/login">go to login</Link>
</span>
</Layout>
);
}
// A layout component to center the content
export function Layout({ children }: { children: React.ReactNode }) {
return (
<div className="w-full h-full bg-white">
<div className="min-w-full min-h-[75vh] flex items-center justify-center">
<div className="w-full h-full max-w-sm p-5 bg-white">
<div>{children}</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
We imported the generated Auth UI components and used them in our pages. Read more about the Auth UI components here.
5. Set up an Email Sender
To support e-mail verification and password reset flows, we need an e-mail sender. Luckily, Wasp supports several email providers out of the box.
We'll use SendGrid in this guide to send our e-mails. You can use any of the supported email providers.
To set up SendGrid to send emails, we will add the following to our main.wasp file:
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
app myApp {
// ...
// 7. Set up the email sender
emailSender: {
provider: SendGrid,
}
}
app myApp {
// ...
// 7. Set up the email sender
emailSender: {
provider: SendGrid,
}
}
... and add the following to our .env.server file:
SENDGRID_API_KEY=<your key>
If you are not sure how to get a SendGrid API key, read more here.
Read more about setting up email senders in the sending emails docs.
Conclusion
That's it! We have set up email authentication in our app. 🎉
Running wasp db migrate-dev and then wasp start should give you a working app with email authentication. If you want to put some of the pages behind authentication, read the using auth docs.
Login and Signup Flows
Login
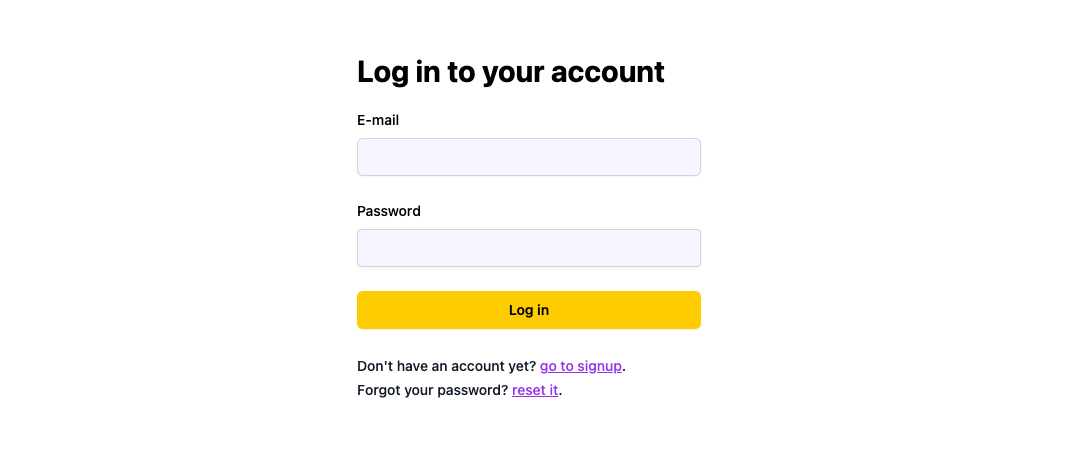
If logging in with an unverified email is allowed, the user will be able to login with an unverified email address. If logging in with an unverified email is not allowed, the user will be shown an error message.
Read more about the allowUnverifiedLogin option here.
Signup
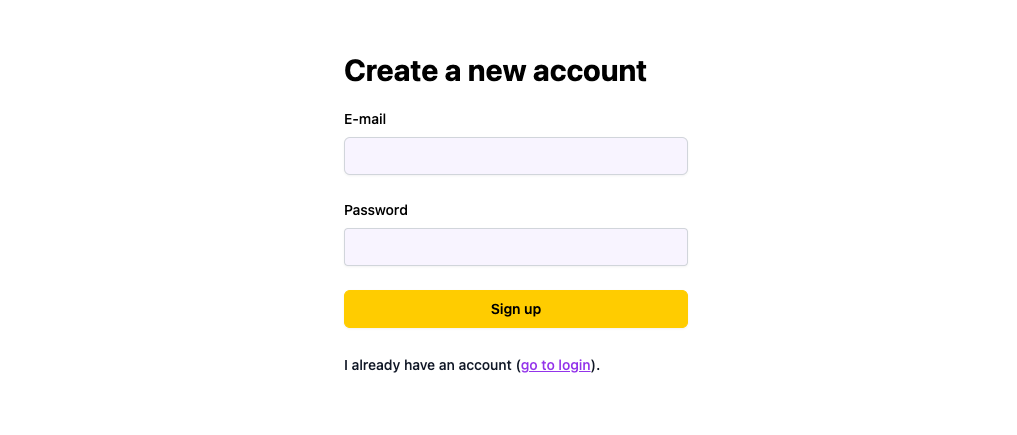
Some of the behavior you get out of the box:
- Rate limiting
We are limiting the rate of sign-up requests to 1 request per minute per email address. This is done to prevent spamming.
- Preventing user email leaks
If somebody tries to signup with an email that already exists and it's verified, we pretend that the account was created instead of saying it's an existing account. This is done to prevent leaking the user's email address.
- Allowing registration for unverified emails
If a user tries to register with an existing but unverified email, we'll allow them to do that. This is done to prevent bad actors from locking out other users from registering with their email address.
- Password validation
Read more about the default password validation rules and how to override them in using auth docs.
Email Verification Flow
By default, Wasp requires the e-mail to be verified before allowing the user to log in. This is done by sending a verification email to the user's email address and requiring the user to click on a link in the email to verify their email address.
Our setup looks like this:
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
// ...
emailVerification: {
clientRoute: EmailVerificationRoute,
}
// ...
emailVerification: {
clientRoute: EmailVerificationRoute,
}
When the user receives an e-mail, they receive a link that goes to the client route specified in the clientRoute field. In our case, this is the EmailVerificationRoute route we defined in the main.wasp file.
The content of the e-mail can be customized, read more about it here.
Email Verification Page
We defined our email verification page in the auth.tsx file.
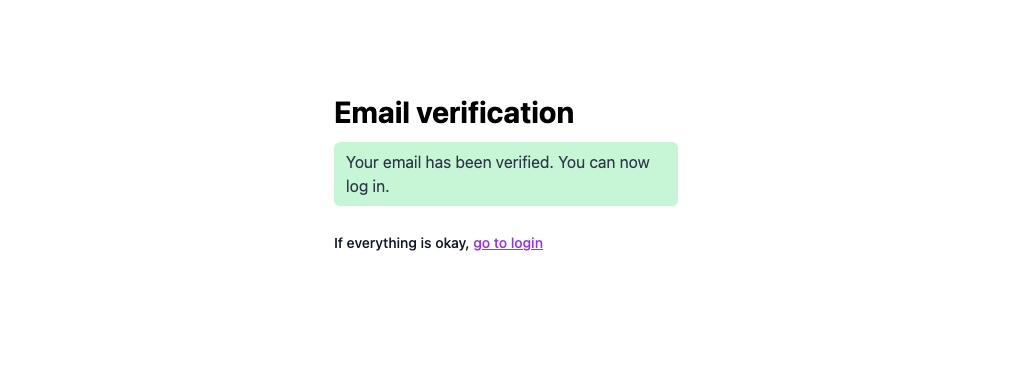
Password Reset Flow
Users can request a password and then they'll receive an e-mail with a link to reset their password.
Some of the behavior you get out of the box:
- Rate limiting
We are limiting the rate of sign-up requests to 1 request per minute per email address. This is done to prevent spamming.
- Preventing user email leaks
If somebody requests a password reset with an unknown email address, we'll give back the same response as if the user requested a password reset successfully. This is done to prevent leaking information.
Our setup in main.wasp looks like this:
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
// ...
passwordReset: {
clientRoute: PasswordResetRoute,
}
// ...
passwordReset: {
clientRoute: PasswordResetRoute,
}
Request Password Reset Page
Users request their password to be reset by going to the /request-password-reset route. We defined our request password reset page in the auth.tsx file.
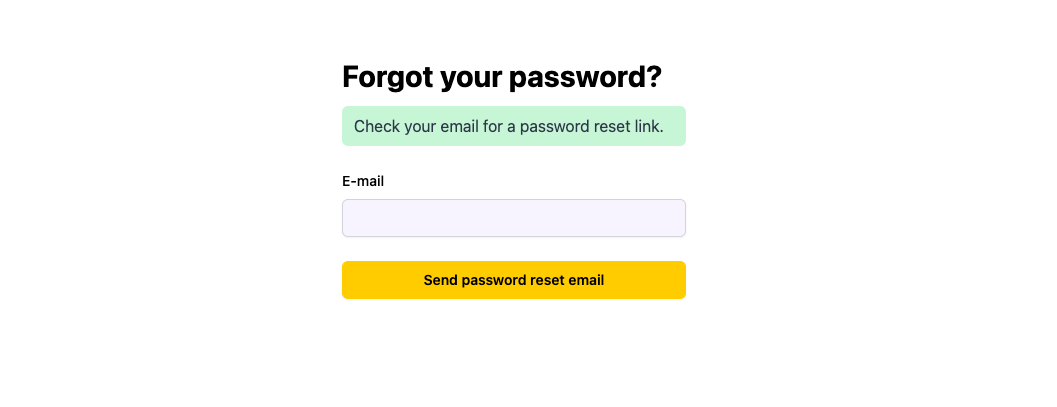
Password Reset Page
When the user receives an e-mail, they receive a link that goes to the client route specified in the clientRoute field. In our case, this is the PasswordResetRoute route we defined in the main.wasp file.
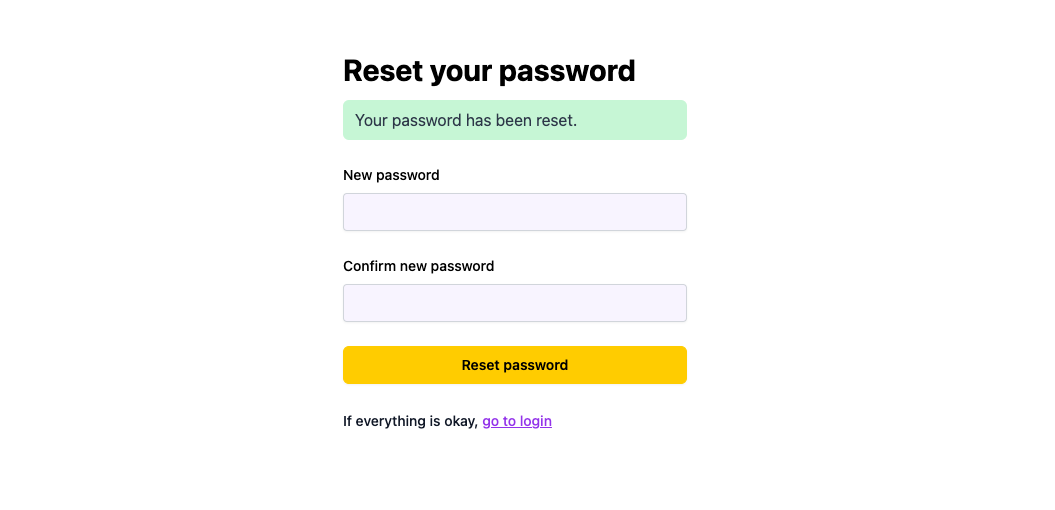
Users can enter their new password there.
The content of the e-mail can be customized, read more about it here.
Using The Auth
To read more about how to set up the logout button and how to get access to the logged-in user in our client and server code, read the using auth docs.
API Reference
Let's go over the options we can specify when using email authentication.
userEntity fields
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
app myApp {
title: "My app",
// ...
auth: {
userEntity: User,
methods: {
email: {
// We'll explain these options below
},
},
onAuthFailedRedirectTo: "/someRoute"
},
// ...
}
// Using email auth requires the `userEntity` to have at least the following fields
entity User {=psl
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
email String? @unique
password String?
isEmailVerified Boolean @default(false)
emailVerificationSentAt DateTime?
passwordResetSentAt DateTime?
psl=}
app myApp {
title: "My app",
// ...
auth: {
userEntity: User,
methods: {
email: {
// We'll explain these options below
},
},
onAuthFailedRedirectTo: "/someRoute"
},
// ...
}
// Using email auth requires the `userEntity` to have at least the following fields
entity User {=psl
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
email String? @unique
password String?
isEmailVerified Boolean @default(false)
emailVerificationSentAt DateTime?
passwordResetSentAt DateTime?
psl=}
Email auth requires that userEntity specified in auth contains:
- optional
emailfield of typeString - optional
passwordfield of typeString isEmailVerifiedfield of typeBooleanwith a default value offalse- optional
emailVerificationSentAtfield of typeDateTime - optional
passwordResetSentAtfield of typeDateTime
Fields in the email dict
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
app myApp {
title: "My app",
// ...
auth: {
userEntity: User,
methods: {
email: {
fromField: {
name: "My App",
email: "hello@itsme.com"
},
emailVerification: {
clientRoute: EmailVerificationRoute,
getEmailContentFn: import { getVerificationEmailContent } from "@server/auth/email.js",
},
passwordReset: {
clientRoute: PasswordResetRoute,
getEmailContentFn: import { getPasswordResetEmailContent } from "@server/auth/email.js",
},
allowUnverifiedLogin: false,
},
},
onAuthFailedRedirectTo: "/someRoute"
},
// ...
}
app myApp {
title: "My app",
// ...
auth: {
userEntity: User,
methods: {
email: {
fromField: {
name: "My App",
email: "hello@itsme.com"
},
emailVerification: {
clientRoute: EmailVerificationRoute,
getEmailContentFn: import { getVerificationEmailContent } from "@server/auth/email.js",
},
passwordReset: {
clientRoute: PasswordResetRoute,
getEmailContentFn: import { getPasswordResetEmailContent } from "@server/auth/email.js",
},
allowUnverifiedLogin: false,
},
},
onAuthFailedRedirectTo: "/someRoute"
},
// ...
}
fromField: EmailFromField required
fromField is a dict that specifies the name and e-mail address of the sender of the e-mails sent by your app.
It has the following fields:
name: name of the senderemail: e-mail address of the sender required
emailVerification: EmailVerificationConfig required
emailVerification is a dict that specifies the details of the e-mail verification process.
It has the following fields:
-
clientRoute: Route: a route that is used for the user to verify their e-mail address. requiredClient route should handle the process of taking a token from the URL and sending it to the server to verify the e-mail address. You can use our
verifyEmailaction for that.- JavaScript
- TypeScript
src/pages/EmailVerificationPage.jsximport { verifyEmail } from '@wasp/auth/email/actions';
...
await verifyEmail({ token });src/pages/EmailVerificationPage.tsximport { verifyEmail } from '@wasp/auth/email/actions';
...
await verifyEmail({ token });noteWe used Auth UI above to avoid doing this work of sending the token to the server manually.
-
getEmailContentFn: ServerImport: a function that returns the content of the e-mail that is sent to the user.Defining
getEmailContentFncan be done by defining a file in theserverdirectory.This is the default content of the e-mail, you can customize it to your liking.- JavaScript
- TypeScript
server/email.jsexport const getVerificationEmailContent = ({ verificationLink }) => ({
subject: 'Verify your email',
text: `Click the link below to verify your email: ${verificationLink}`,
html: `
<p>Click the link below to verify your email</p>
<a href="${verificationLink}">Verify email</a>
`,
})server/email.tsimport { GetVerificationEmailContentFn } from '@wasp/types'
export const getVerificationEmailContent: GetVerificationEmailContentFn = ({
verificationLink,
}) => ({
subject: 'Verify your email',
text: `Click the link below to verify your email: ${verificationLink}`,
html: `
<p>Click the link below to verify your email</p>
<a href="${verificationLink}">Verify email</a>
`,
})
passwordReset: PasswordResetConfig required
passwordReset is a dict that specifies the password reset process.
It has the following fields:
-
clientRoute: Route: a route that is used for the user to reset their password. requiredClient route should handle the process of taking a token from the URL and a new password from the user and sending it to the server. You can use our
requestPasswordResetandresetPasswordactions to do that.- JavaScript
- TypeScript
src/pages/ForgotPasswordPage.jsximport { requestPasswordReset } from '@wasp/auth/email/actions';
...
await requestPasswordReset({ email });src/pages/PasswordResetPage.jsximport { resetPassword } from '@wasp/auth/email/actions';
...
await resetPassword({ password, token })src/pages/ForgotPasswordPage.tsximport { requestPasswordReset } from '@wasp/auth/email/actions';
...
await requestPasswordReset({ email });src/pages/PasswordResetPage.tsximport { resetPassword } from '@wasp/auth/email/actions';
...
await resetPassword({ password, token })noteWe used Auth UI above to avoid doing this work of sending the password request and the new password to the server manually.
-
getEmailContentFn: ServerImport: a function that returns the content of the e-mail that is sent to the user.Defining
getEmailContentFnis done by defining a function that looks like this:This is the default content of the e-mail, you can customize it to your liking.- JavaScript
- TypeScript
server/email.jsexport const getPasswordResetEmailContent = ({ passwordResetLink }) => ({
subject: 'Password reset',
text: `Click the link below to reset your password: ${passwordResetLink}`,
html: `
<p>Click the link below to reset your password</p>
<a href="${passwordResetLink}">Reset password</a>
`,
})server/email.tsimport { GetPasswordResetEmailContentFn } from '@wasp/types'
export const getPasswordResetEmailContent: GetPasswordResetEmailContentFn = ({
passwordResetLink,
}) => ({
subject: 'Password reset',
text: `Click the link below to reset your password: ${passwordResetLink}`,
html: `
<p>Click the link below to reset your password</p>
<a href="${passwordResetLink}">Reset password</a>
`,
})
allowUnverifiedLogin: bool: specifies whether the user can login without verifying their e-mail address
It defaults to false. If allowUnverifiedLogin is set to true, the user can login without verifying their e-mail address, otherwise users will receive a 401 error when trying to login without verifying their e-mail address.
Sometimes you want to allow unverified users to login to provide them a different onboarding experience. Some of the pages can be viewed without verifying the e-mail address, but some of them can't. You can use the isEmailVerified field on the user entity to check if the user has verified their e-mail address.
If you have any questions, feel free to ask them on our Discord server.